Qt로 리눅스 마우스 매크로를 만드는 방법입니다. 리눅스는 마우스, 키보드와 같은 이벤트들도 파일로 처리가 되기 때문에 file open -> read / write 식으로 흘러가게 됩니다.
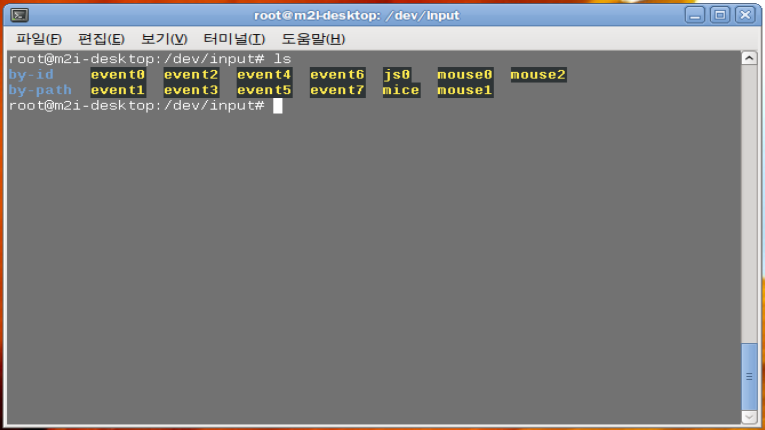
그러면 그 이벤트의 파일을 확인하기 위해서는 /dev/input 경로로 들어갑니다.
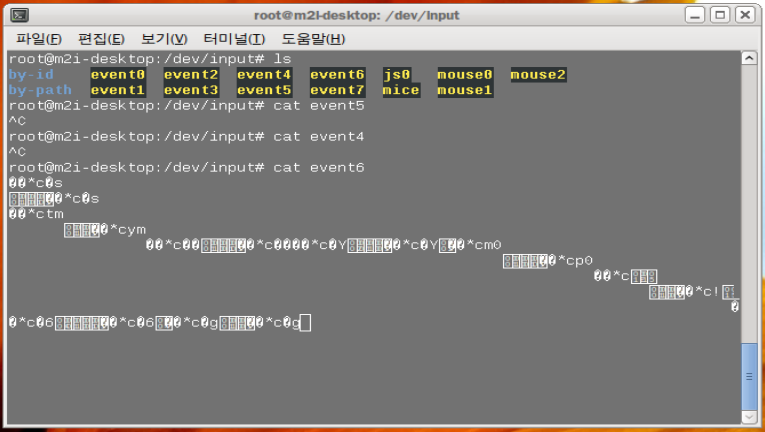
ls 시 아래처럼 여러 이벤트, 장치 파일이 있을텐데 cat으로 파일을 읽어봅니다.
실행 후 마우스 클릭같은 이벤트 발생시켜보면 특정 이벤트에선 알수없는 문자들이 호출되는데 이 이벤트가 해당 마우스 이벤트라고 보시면 됩니다.
이제 마우스 이벤트의 파일을 확인했으니 file을 open합니다.
void MainWindow::LoadMouse()
{
m_sMousePath = "/dev/input/event6";
if ( (fd= open(m_sMousePath.toLatin1().data(), O_RDWR)) == -1 ) {
QMessageBox::critical(this, "Open Error", "Open Error - Check Touch Device Path");
QTimer::singleShot(100, this, SLOT(close()));
}
}그리고 mouse 이벤트를 받을 쓰레드를 하나 만들어 따로 돌리겠습니다. 쓰레드를 사용하는 이유는 read 시 block 처리가 되기 때문에 특정 이벤트가 n초간 발생하지 않으면 사이클이 끝났다고 판단하게 처리하기 위함입니다.
#ifndef GETMOUSEEVENTTHREAD_H
#define GETMOUSEEVENTTHREAD_H
#include <QThread>
#include "linux/input.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
enum NState {
enReady = 0, // Record 버튼 눌렀을 때 이벤트 버리기 위함
enGetInput = 1
};
class GetMouseEventThread : public QThread
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit GetMouseEventThread(QObject *parent = 0, int fd = 0, QString sPath = "");
~GetMouseEventThread();
void SetState(int State);
int GetState() { return m_nState; }
int inputListCount();
struct input_event GetInputData(int nIndex);
bool WaitFor(unsigned long time = ULONG_MAX);
private:
void run();
int m_nState;
int m_nfd;
QString m_sMousePath; // 터치 장치 경로
QList<struct input_event> inputList; // 터치 이벤트 저장 용
signals:
void Emit_readRefresh();
public slots:
};
#endif // GETMOUSEEVENTTHREAD_H#include "GetMouseEventThread.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include "unistd.h"
GetMouseEventThread::GetMouseEventThread(QObject *parent, int fd, QString sPath) :
QThread(parent),
m_nfd(fd),
m_sMousePath(sPath)
{
}
GetMouseEventThread::~GetMouseEventThread()
{
}
void GetMouseEventThread::SetState(int State)
{
m_nState = State;
}
int GetMouseEventThread::inputListCount()
{
return inputList.count();
}
input_event GetMouseEventThread::GetInputData(int nIndex)
{
struct input_event event;
event = inputList.value(nIndex);
return event;
}
void GetMouseEventThread::run()
{
inputList.clear();
struct input_event input;
while ( read(m_nfd, &input, sizeof(struct input_event)) ){
if ( m_nState == enGetInput ) {
inputList.append(input);
}
emit Emit_readRefresh();
}
}
bool GetMouseEventThread::WaitFor(unsigned long time)
{
bool bResult = false;
bResult = wait(time);
return bResult;
}위 쓰레드는 2가지 상태를 가집니다. 상태를 굳이 구분해 놓은 이유는 Record 라는 버튼을 클릭하는 이벤트도 기록이 되기 때문에 그 이벤트를 먼저 비우기 위함입니다. 상태가 GetInput일 경우에만 이벤트 리스트에 담고 read가 성공했을 때는 MainWindows에 emit을 날려줍니다.
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include <QMainWindow>
#include <QTimer>
#include "GetMouseEventThread.h"
#include "linux/input.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
const int nWaitTime = 10;
const int nCycleTime = 20;
enum NRunState {
enStop = 0,
enRun = 1
};
enum NRecordState {
enOff = 0,
enOn = 1
};
namespace Ui {
class MainWindow;
}
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0);
~MainWindow();
void InitUI();
void LoadMouse();
private:
Ui::MainWindow *ui;
bool m_bRunState;
bool m_bRecordState;
QString m_sMousePath; // 터치 장치 경로
int fd;
QTimer MacroTimer; // Cycle 타이머
QTimer recordTimer; // ReadThread 갱신 확인용
GetMouseEventThread* pReadThread; // 터치 이벤트 read 용
public slots:
void Slot_Click_RunStop();
void Slot_Click_Record();
void Slot_MacroOn();
void Slot_recordTimerReFresh();
void Slot_recordTimeout();
};
#endif // MAINWINDOW_H#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QSettings>
#include <QMessageBox>
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow),
m_bRunState(enStop),
m_bRecordState(enOff)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
setWindowFlags( Qt::WindowStaysOnTopHint);
InitUI();
LoadMouse();
pReadThread = new GetMouseEventThread(this, fd, m_sMousePath);
connect(pReadThread, SIGNAL(Emit_readRefresh()), this, SLOT(Slot_recordTimerReFresh()), Qt::UniqueConnection);
connect(pReadThread, SIGNAL(terminated()), this, SLOT(Slot_threadTerminated()), Qt::UniqueConnection);
connect(&MacroTimer, SIGNAL(timeout()), this, SLOT(Slot_MacroOn()), Qt::UniqueConnection);
connect(&recordTimer, SIGNAL(timeout()), this, SLOT(Slot_recordTimeout()), Qt::UniqueConnection);
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
if ( pReadThread->isRunning() ) {
pReadThread->WaitFor();
}
if ( pReadThread != NULL ) { delete pReadThread; }
}
void MainWindow::InitUI()
{
ui->pbRunStop->setText("Run");
ui->pbRecord->setText("Record");
connect(ui->pbRunStop, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(Slot_Click_RunStop()), Qt::UniqueConnection);
connect(ui->pbRecord, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(Slot_Click_Record()), Qt::UniqueConnection);
}두 타이머는 기록이 끝났는지를 체크하기 위한 타이머와 사이클을 반복하기 위한 타이머로 구성되어 있습니다. Thread에서 emit을 통해 시그널을 받으면 계속해서 recordTimer를 갱신시켜주고 10초로 설정한 recordTimer가 timeout이 됐을 때는 녹화가 종료됩니다.
void MainWindow::Slot_recordTimerReFresh()
{
recordTimer.start(); // ReadThread 갱신 확인
}
void MainWindow::Slot_recordTimeout()
{
if ( pReadThread == NULL ) { return; }
pReadThread->terminate();
if ( pReadThread->GetState() == enReady ) {
pReadThread->SetState(enGetInput);
ui->statusBar->showMessage("No Action for 10 Sec, the recording stops.");
recordTimer.setInterval(10000);
recordTimer.start();
pReadThread->start();
} else {
m_bRecordState = enOff;
ui->pbRecord->setText("Record");
ui->statusBar->showMessage("");
ui->pbRunStop->setEnabled(true);
}
}마지막으로 Macrotimer에서는 받아온 이벤트 리스트들을 실행해 줍니다. 이 이벤트들도 open한 파일 디스크립터에 write 해주는 방식으로 진행합니다.
void MainWindow::Slot_MacroOn()
{
if ( m_bRunState == enStop ) { return; }
int nInputLIstCount = pReadThread->inputListCount();
for ( int i =0; i < nInputLIstCount - 1; i++) {
struct input_event currentinput = pReadThread->GetInputData(i);
struct input_event nextinput = pReadThread->GetInputData(i+1);
struct timeval currentTime = currentinput.time;
struct timeval nextTime = nextinput.time;
write(fd, ¤tinput, sizeof(input_event));
QApplication::processEvents();
uint nDelayTime = (nextTime.tv_sec - currentTime.tv_sec) * 1000000 + nextTime.tv_usec - currentTime.tv_usec;
usleep(nDelayTime);
}
MacroTimer.setInterval(nCycleTime * 1000);
MacroTimer.start();
}timeval 구조체와 input_event 구조체를 한번 살펴보겠습니다. input_event는 이벤트에 대한 정보들이 기록되는데 멤버로 time 정보들도 갖고 있습니다. 이를 통해서 이벤트들 사이의 간격을 구할 수 있는데 그 간격을 sleep을 주게 되면 기록한 사이클을 재현할 수 있게 됩니다.
struct input_event{
struct timval time;
unsigned short type;
unsigned short code;
unsigned int value;
};
struct timeval {
long tv_sec;
long tv_usec;
}
'Programming > Qt' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Qt] QML(0) - Qt Quick Application 시작하기 (1) | 2023.03.20 |
|---|---|
| [Qt] QAbstractItemModel 적용된 View 폰트 변경 (0) | 2022.12.07 |
| Qt Grid Layout addWidget 시 Span 조절 (0) | 2022.09.01 |
| Qt Creator white space 표시 제거 (0) | 2022.01.18 |
| Qt ToolTip (0) | 2021.08.17 |